Understanding Hair Loss in Women: Causes and Treatment Options | Your Complete Guide
Hair Loss in Women
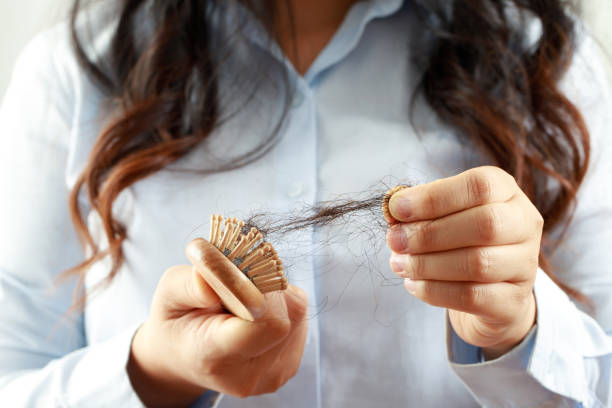
Hair loss is a widespread concern that can affect people of any gender. While men are more likely to experience baldness, hair loss in women is also prevalent and can be a distressing condition. In addition, hair loss can have an impact on a woman’s self-esteem and confidence regardless of her age.
Introduction
Hair loss in women is a complex issue, and various factors can cause it. This article will discuss the causes, types, and risk factors associated with hair loss in women. We will also explore the different treatment options, including medical and non-medical treatments, surgical procedures, and self-care and home remedies. Additionally, we will address coping mechanisms, the psychological effects of hair loss, and the importance of seeking professional help.
Definition of Hair Loss in Women
Hair loss is excessive shedding, resulting in thinning or bald patches on the scalp or other body parts. Hair loss in women can occur for various reasons, including hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, stress, and medical conditions.
Statistics on Hair Loss in Women
The American Hair Loss Association reports that around 40% of women will experience hair loss by the time they reach the age of 40. By age 65, that number increases to 80%. The statistics show that hair loss in women is a prevalent condition affecting many women.
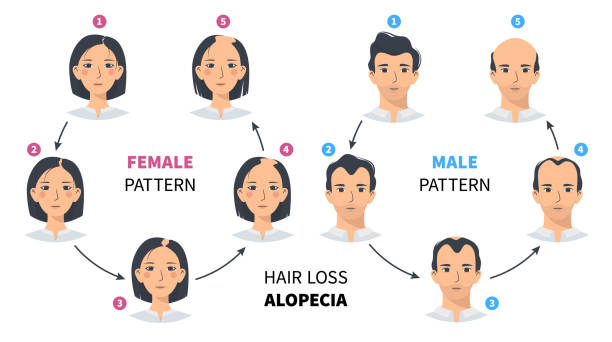
Risk Factors and Contributing Factors
Several risk factors and contributing factors can increase women’s hair loss risk. These include genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, medications, and certain medical conditions.
Genetic Predisposition:
A family history of hair loss can increase women’s risk of developing hair loss.
Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal imbalances, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can cause hair loss in women.
Nutritional Deficiencies:
Nutritional deficiencies such as iron deficiency, or lack of amino acids, can also lead to hair loss in women. Adequate levels of iron are essential for maintaining healthy hair growth. When there is an insufficient amount of iron in the body, hair may become weak and brittle, ultimately resulting in hair loss. In addition, a lack of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein, can also result in hair loss.
If you suspect that a nutritional deficiency causes your hair loss, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider. They can perform blood tests to check for defects and recommend dietary changes or supplements to address deficiencies.
Medications:
Certain medications can also cause hair loss in women. For example, some types of birth control pills can lead to hair loss, as can medications used to treat heart disease or high blood pressure. In addition, cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation can also cause hair loss. Consult your physician if you notice hair loss while on medication and ask if there are alternative treatments that do not have this side effect.
Certain Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions can also cause hair loss in women. For example, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to hormone imbalances that result in hair loss. Cicatricial alopecia, an autoimmune condition, can cause hair follicles to become inflamed and scarred, leading to permanent hair loss. An underactive thyroid or high fever can also cause hair loss. If you have an underlying medical condition, treating the disease may help to slow or stop hair loss.
Diagnosis
Consulting with a healthcare provider to identify the root cause of hair loss is crucial. Several diagnostic tools may be used to determine the cause of hair loss:
Physical Examination:
During a physical examination, a dermatologist or other healthcare provider will examine the scalp to look for signs of hair loss. They may also investigate different body areas for signs of medical conditions contributing to hair loss.
Blood Tests:
Blood tests can check for nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, and other medical conditions causing hair loss.
Scalp Biopsy:
A scalp biopsy may be performed to examine the hair follicles more closely. During this procedure, a small piece of skin is removed from the scalp and examined under a microscope for signs of hair loss or other medical conditions.
Hair Loss Treatment
Several treatments are available for hair loss in women, including medical, non-medical, and surgical treatments.
Medical Treatments:
Minoxidil (Rogaine) is an FDA-approved medication used to treat hair loss in women. It is a topical treatment applied directly to the scalp, and it can help stimulate hair growth and prevent further hair loss. Spironolactone, a medication primarily used to manage hypertension, can also be effective in treating hair loss in women. However, it should not be used during pregnancy.
Non-Medical Treatments:
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and adipose-derived stem cell protein extract (AAPE) are non-medical treatments that can treat hair loss in women. PRP involves:
- Drawing a small amount of blood from the patient.
- Processing it to concentrate the platelets.
- Injecting the concentrated platelets into the scalp.
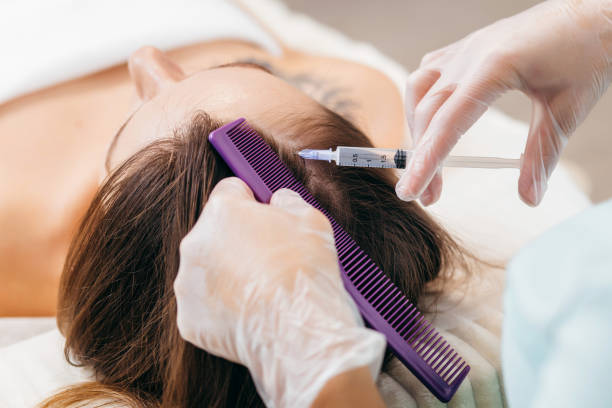
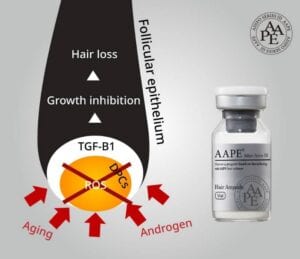
AAPE (Advanced Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Protein Extract) treatment for hair loss involves using stem cells extracted from adipose (fat) tissue to stimulate hair growth. This treatment involves injecting the AAPE solution directly into the scalp, where it can stimulate the hair follicles and promote new hair growth.
AAPE therapy is a minimally invasive treatment that has shown promising results in clinical studies, with some patients experiencing significant hair regrowth after just a few sessions. Despite being a relatively new therapy for hair loss, AAPE treatment has shown potential as a safe and effective alternative to more invasive procedures like hair transplant surgery.
Surgical Treatments:
Hair transplant surgery is a type of surgical treatment that is often reserved for more advanced cases of hair loss. A hair transplant is a procedure that entails the extraction of hair follicles from a donor area of the scalp and their transplantation to an area where hair growth is weak or absent. It is generally performed in cases of more advanced hair loss.
Two primary types of hair transplant surgery are available: Follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE) are two main techniques used in hair transplant surgery. The FUT technique involves removing a strip of skin from the scalp, which is then divided into smaller grafts and transplanted into the area with weak or absent hair growth.
FUE involves extracting hair follicles from the scalp and transplanting them directly into the affected area. Hair transplant surgery is often considered an effective option for treating hair loss, as the transplanted hair can closely resemble natural hair in appearance and behavior.
It is crucial to consider that the success of hair transplant surgery depends on various factors, including the surgeon’s skill and experience, the extent of hair loss, the amount of available donor hair, and the patient’s age and overall health.
Hair transplant surgery usually takes several hours to complete and is typically performed under local anesthesia. The length of recovery time after hair transplant surgery can vary from person to person, but typically patients can resume work and normal activities within one to two weeks. It is crucial to adhere to all post-operative instructions given by the surgeon to ensure a successful recovery and optimal results.
While hair transplant surgery can be an effective treatment option, it is essential to carefully consider the risks and potential side effects before undergoing the procedure. These can include scarring, infection, bleeding, and the possibility of the transplanted hair not taking root and falling out. Therefore, it is essential to consult with a qualified and experienced surgeon to discuss the procedure’s benefits and risks and determine if it is the right option for you.
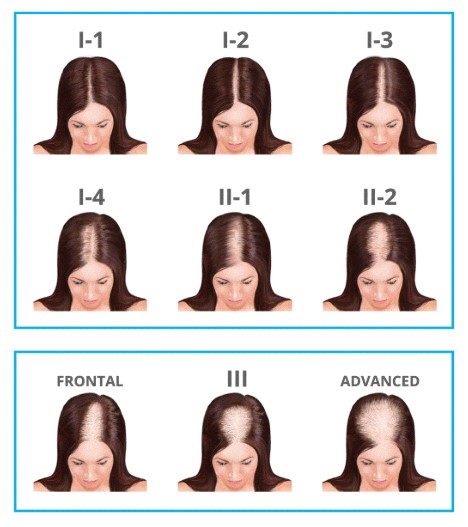


Self-Care and Home Remedies:
Several self-care and home remedies can improve the appearance and health of hair, in addition to medical and surgical treatment options for hair loss in women. These include:
Hair care tips:
Proper hair care can help prevent damage and breakage, which can contribute to hair loss. Self-care and home remedies for hair loss in women include adopting a gentle hair care routine with a mild shampoo and conditioner, avoiding the use of heat styling tools, and using a wide-toothed comb to gently detangle wet hair.
Lifestyle changes:
Healthy lifestyles can also contribute to healthy hair growth. A lifestyle that includes a healthy balanced diet rich in vital nutrients, regular exercise, and effective stress management can aid in the prevention and treatment of hair loss.
Natural remedies:
One can find many natural remedies that are traditionally used to prevent hair loss and stimulate hair growth. These include supplements such as biotin, saw palmetto and essential oils such as lavender and rosemary. Although self-care and home remedies may not guarantee to prevent or reverse hair loss, they can help enhance the overall health and appearance of the hair.
Coping with Hair Loss:
Hair loss can have significant psychological effects on women, including decreased self-esteem and feelings of anxiety and depression. Therefore, it is essential for women experiencing hair loss to seek support and resources to help them cope with the emotional impact of the condition.
Psychological effects:
Hair loss can significantly impact a woman’s self-esteem and body image. Recognizing and addressing the emotional impact of hair loss is crucial for women, and seeking support from loved ones or a mental health counsellor may be necessary.
Support groups:
Several support groups and organizations are dedicated to providing resources and support to women experiencing hair loss. These can be a valuable source of information and community for women going through a difficult time.
Cosmetic solutions:
Several cosmetic solutions can help women cope with the appearance of hair loss. These include wigs, hairpieces, and hair extensions, as well as scalp micropigmentation and cosmetic tattooing:
Wigs and hairpieces:
Hairpieces and wigs and can provide temporary relief for women who are dealing with hair loss. They come in various styles and colours to match your natural hair and can be easily removed or changed. Wigs can be made from synthetic materials or human hair and range in price from affordable to very expensive.
Hair extensions:
Hair extensions are a popular cosmetic solution for women with thinning hair. They can add volume and length to existing hair, making it appear fuller and thicker. Hair extensions can be made from human hair or synthetic materials and attached using various methods such as clips, tape, or glue.
Scalp micropigmentation:
Scalp micropigmentation (SMP) is a cosmetic tattooing procedure that involves using tiny needles to create the appearance of hair follicles on the scalp. One can effectively create the illusion of a full head of hair or hide bald spots or scars from hair transplant surgery using wigs and hairpieces. SMP is a non-surgical, non-invasive treatment that typically requires multiple sessions to achieve optimal results.
Cosmetic tattooing:
Cosmetic tattooing, commonly known as permanent makeup, can be utilized to mimic the appearance of thicker eyebrows or eyelashes or conceal any skin scars or discolorations. It involves implanting pigment into the skin using a thin needle and can last several years before needing a touch-up.
While these cosmetic solutions can help women cope with the appearance of hair loss, it’s important to remember that they do not address the underlying cause of the hair loss itself. Therefore, issuing high-quality products and services from reputable providers is essential to ensure the best possible results.
Q & A
Q: What can cause hair loss in women?
A: Hair loss in women can be caused by various factors, including genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, certain medical conditions, medications, nutritional deficiencies, and lifestyle factors.
Q: Why am I suddenly losing so much hair?
A: Sudden hair loss can be caused by several factors, including hormonal changes, stress, nutritional deficiencies, and medical conditions. Therefore, seeing a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment is essential.
Q: How can I stop my hair from falling out, female?
A: The best way to prevent hair loss in women is to address the underlying cause. This may include treating medical conditions, improving nutrition, reducing stress, and using hair care products that are gentle on the scalp.
Q: Which vitamin deficiency causes hair loss?
A: Vitamin D, vitamin B12, and iron deficiencies have all been linked to hair loss in women.
Q: How common is hair loss in women?
A: Hair loss is a common problem for women, affecting up to 50% of women at some point.
Q: What causes hair loss in women in their 20s?
A: Hair loss in women in their 20s can be caused by various factors, including genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, stress, and nutritional deficiencies.
Q: Is PRP suitable for female hair loss?
A: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy effectively treats hair loss in women, particularly in cases of androgenetic alopecia. However, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to determine if PRP is the right treatment option for your needs.
Takeaway
Hair loss caused by androgenic alopecia is the most frequently occurring type in both men and women. Male pattern hair loss is an androgenic alopecia affecting more than 50% of men over 50. For women, other common causes include stress, hormonal issues, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medications.
- The androgenic alopecia medical term refers to hair thinning and pattern baldness caused by genetic and hormonal factors. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential; seeking professional help from a dermatologist or healthcare provider is a good idea.
- Blood tests can check hormone levels and rule out underlying health conditions contributing to hair loss. The immune system plays a role in hair growth, as does the anagen phase of the growth cycle.
- Treatment options for androgenic alopecia include oral contraceptives, cyproterone acetate, and spironolactone to manage hormonal imbalances contributing to hair loss.
- Minoxidil can stimulate new hair growth by targeting vellus hairs, which are delicate and light-coloured, and making them thicker and darker. Surgical options like hair transplant surgery may also be considered in more advanced hair loss cases.
- Nutritional supplements can also help manage hair loss. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends treating androgenic alopecia with minoxidil or cyproterone acetate.
- Non-medical treatments such as PRP and AAPE are also available. Lifestyle changes such as keeping a healthy diet, reducing stress, and avoiding harsh hair treatments can also help manage hair loss.
- Early treatment is crucial to slow or stop hair loss and promote regrowth. Clinical trials are exploring new hair loss treatments targeting the androgen hormones responsible for male pattern baldness.
- It’s essential to seek professional help from a dermatologist or healthcare provider if you’re experiencing noticeable hair loss. A blood test and a medical history review can help determine the underlying causes of hair loss.
- Hormone levels, including male sex hormones and androgen levels, can also be tested. Different hair loss patterns may indicate various reasons, and treatment of androgenetic alopecia should be tailored accordingly.
- Loose hairs during the telogen phase of the hair growth cycle are also common. With the proper hair loss treatment and support, both men and women can regain the appearance of a full head of hair.
The good news is that hair loss treatments have come a long way, and ongoing research and clinical trials offer hope for even more effective treatments. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also help promote hair growth and regrowth.
FREE ONLINE ASSESSMENT FORM
Book Your Free Consultation Today Or Call (647) 492-9093
Female Pattern Hair Loss: A clinical, pathophysiologic, and …
Could it be female pattern hair loss?
Comments are closed.