Table of Contents
Androgenetic Hair Loss – Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic hair loss, also known as male or female pattern hair loss, is a common type of hair loss characterized by gradually thinning the hair on the scalp. It is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors and is thought to be influenced by the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the scalp.
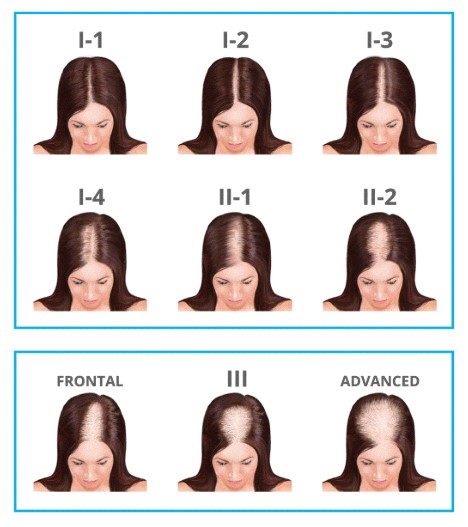
Androgenetic hair loss is more common in men than in women, but it can affect people of both genders. In men, androgenetic hair loss typically presents as a receding hairline and thinning of the hair on the crown of the head. In women, it is more likely to present as diffuse thinning of the hair on the scalp.
What is the best treatment for androgenetic hair loss?
Androgenetic hair loss is typically treated with medications such as finasteride or minoxidil, which can help to slow the progression of hair loss and stimulate new hair growth. In some cases, a combination of medications and other treatments, such as PRP (platelet-rich plasma) treatment or hair transplantation, may be recommended. It is essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of different treatment options with a trichologist to determine the most appropriate course of treatment for your individual situation.
Is androgenetic hair loss reversible?
Androgenetic hair loss is not reversible, but it can be treated with medications or other therapies that can help to slow the progression of hair loss and stimulate new hair growth.
What causes androgenic hair loss?
Androgenetic alopecia is a common hair loss caused by genetic and hormonal factors. It is thought to be influenced by the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the scalp.
DHT is a derivative of the hormone testosterone produced in the hair follicles and prostate gland. In people with androgenetic hair loss, the hair follicles are sensitive to the effects of DHT, which causes them to shrink and produce finer, shorter hairs. Over time, this can lead to a gradual thinning of the hair on the scalp.
How do you know if your hair loss is androgenic?
To determine if your hair loss is androgenetic, a trichologist can physically examine your scalp and hair and ask about your medical history and any medications you are taking. They may also order blood tests to check your hormone levels and rule out other potential causes of hair loss, such as iron deficiency or an underlying medical condition.
If you are experiencing hair loss and are concerned about its cause, you should consult a trichologist for a proper assessment and treatment recommendations.
What causes androgenetic alopecia in females?
Androgenetic alopecia for women, also known as female pattern hair loss, is a common type of hair loss that affects women. It is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors and is thought to be influenced by the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the scalp.
It is thought that a person’s genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining their risk of developing androgenetic alopecia. Other factors, such as age and hormonal changes, can also contribute to the development of androgenetic alopecia in women.
FREE ONLINE HAIR LOSS ASSESSMENT Toronto Trichology Centre | Hair Loss Clinic
Comments are closed.