Table of Contents
Hair Transplantation: Restoring Confidence with Permanent Results
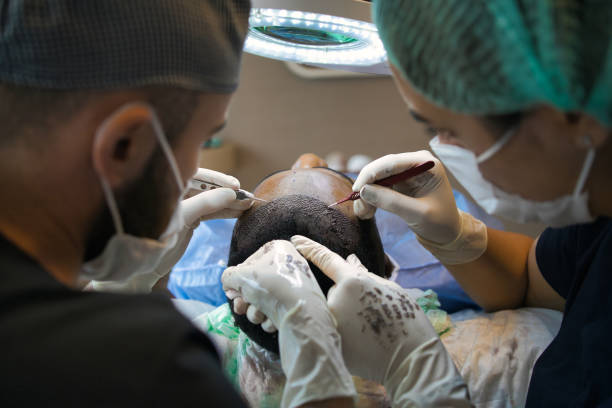
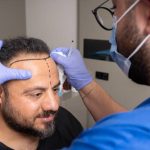
Hair transplant surgery is a procedure for hair restoration that is appropriate for individuals of both genders who experience pattern hair loss. To be a candidate for a hair transplant, an individual must have an adequate donor area with healthy hair follicles to be removed. Two of the most popular hair transplant systems are Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT).
FUE hair transplant procedures extract individual hair follicles from the donor area and transplant them to areas of the scalp that are experiencing hair loss. In contrast, FUT entails extracting a strip of skin containing donor hair and dividing it into separate follicular units. Both methods require precision and skill from the surgeon to achieve natural-looking results.
After the hair transplant surgery, the transplanted hair follicles will fall out, and patients will experience temporary shedding. However, this is a normal part of the hair growth cycle, and new hair growth will eventually begin within a few months. Patients can expect to return to work within a week or two after the procedure, with some minor side effects such as swelling and redness around the treated areas.
If you are thinking about getting a Toronto hair transplant, it is essential to choose a reputable hair transplant clinic where experienced surgeons can assess if you are a good candidate for the procedure and recommend the appropriate type of hair transplant based on your hair type and pattern of hair loss. With the help of a hair transplant, you can achieve a natural-looking hairline and regain your confidence.
For people who are bothered by baldness or thinning hair, hair transplantation is a recommended treatment. This treatment method involves moving hair from thicker regions of the scalp to areas of the scalp that lack hair through cosmetic surgery. Usually, multiple transplant procedures are required, which can be costly. Results, however, are typically positive and long-lasting.
What can I do to get ready for a hair transplant?
Inform your surgeon of any current or former medical conditions, as well as any medicines you are taking (including over-the-counter items and herbal remedies). The danger of bleeding is increased by some medications. Some medications may need to be briefly stopped.
It is preferable if you quit smoking. Smoking has an impact on how wounds recover and raises the danger of bleeding and infection after surgery.
The procedure for a hair replacement, what happens?
You will typically be sedated and given a topical anesthetic. You might receive a general anesthetic if the operation you are having is complicated.
Several distinct surgical methods could be employed, including:
- Inserting hair plugs from places where it is still growing into bald spots.
- Transplanting tiny skin sections from hairier regions.
- Areas of bald epidermis are removed during scalp reduction.
Consult your physician to learn what they might advise.
After a hair replacement, what should I anticipate?
Following the process, you might experience discomfort like a tight feeling or aching in your head. It’s possible that you’ll need to take painkillers. You’ll need someone to help drive you home and remain with you at first. Your surgeon will provide you with directions, such as when to start exercising again, when to have any stitches removed, and when to wash your hair.
Is there anything that could possibly go wrong?
Even though the majority of patients bounce back quickly from surgery, some may experience bleeding, an illness, thick scars, or a patchy appearance. For some individuals, hair growth is slower than they had anticipated. Some choose to have the procedure repeated if they discover it is unsuccessful. Plastic surgery is no small procedure. An anesthetist should be present during cosmetic procedures performed by experienced surgeons in accredited facilities.
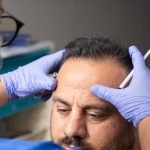
What a hair transplant entails
A local anesthetic and sedative are typically used during a hair transplant, so you’ll be awake but not in discomfort.
A hair transplant can be one of two kinds:
Strip technique or follicular unit transplantation (FUT); Hair grafts are created by dividing a thin strip of hair-covered skin from the back of your head into pieces. These pieces, each containing one to four hairs, are then inserted into tiny scalp indentions. There will be a mark on the back of your head where the hairs are removed from, but unless you have very short hair, it shouldn’t be noticeable. Only the region where the skin has been removed needs to be trimmed; the skull does not need to be shaved.
FUE: Follicular unit excision; Hair is shaved off the back of the skull. Individual hairs are removed one at a time (grafts), and the grafts are inserted into small cuts made in the scalp. There will be numerous small scars, but they won’t be particularly noticeable. The average hair transplant procedure lasts a day, but you shouldn’t have to remain overnight. You might need to schedule two or more sessions spaced out by a few months if a sizable region needs to be treated. How to take care of your graft will be explained by your physician. To aid in recovery and hair growth, you should be provided a spray to use.
Recovery
- The average recovery time for hair transplant patients is three days. For the first two weeks following your procedure, you must be extremely cautious with your newly transferred hair. They won’t be stable implants.
- To minimize scarring, you might be advised to decrease your exercise during the first month.
- Any bandages can typically be taken off after 2 to 5 days, but you shouldn’t handle the grafts.
- From day 6 you should be able to carefully hand-wash your hair.
- Any non-dissolvable sutures can typically be removed after 10 to 14 days.
- The transplanted hair frequently starts to come out after a few weeks and then begins to grow back.
- New hair will typically start to grow after six months.
- The full effects ought to be visible after 12 to 18 months.
Expected side effects
- Following a hair transplant, it’s typical to experience: a tight, painful, and swollen head for a few days.
- Transient scabbing at the transplanted hair site.
- A solitary scar or several extremely small scars.
- Although a hair transplant is typically a safe procedure, there is always a small risk of bleeding, infection, and an allergic reaction to the anesthetic. Your surgeon should be able to quickly address these issues.
- Additionally, there is a slight possibility that the transfer will fail and the hair will fall out or leave a visible scar.
- The likelihood of these issues and the recommended course of treatment should be discussed with your physician.
- You might still lose hair around the implant.
- To ensure that the hair appears natural over time, your surgeon should carefully plan the layout of the transplant.
Comments are closed.