July 24, 2023 By simonw Comments are Off
Table of Contents
Introduction to Seborrheic Dermatitis
The Basic Definition of Seborrheic Dermatitis
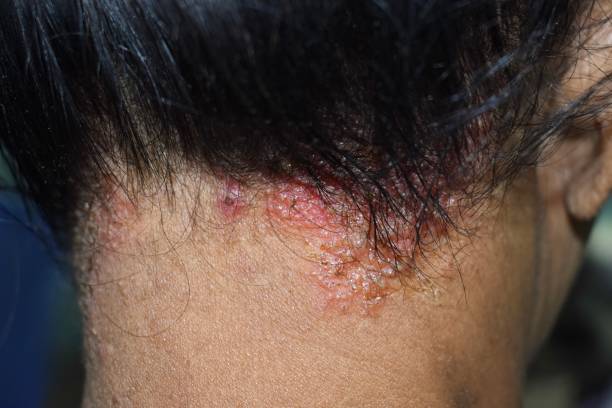
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD), also referred to as seborrheic eczema or seborrhoeic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that primarily affects oily areas of the body, such as the scalp, face, chest, and creases of the arms, legs, and diaper area. It is characterized by inflammation of the upper layers of skin, presenting as a red scaly rash with greasy scales, and is often accompanied by an itchy rash and redness. It shares many clinical characteristics with other skin conditions like psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and allergic contact dermatitis.
Common Symptoms and Signs of Seborrheic Dermatitis
The condition is typically marked by an itchy, red rash with a characteristic scaly appearance, mainly found on the scalp but also commonly seen in the eyebrows, around the nose, behind the ears, and on the chest. The severity of symptoms associated with seborrheic dermatitis can vary widely, with extreme cases leading to widespread redness and oily skin scattered with white or yellow flaky scales. Such symptoms are prone to intensify with hormonal fluctuations, emotional strain, or colder climates; the condition can often remain prevalent for an extended duration.
The Demographics Mostly Affected by Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis affects people of all ages, but certain demographics are more prone to the condition. For instance, infants under three months old may develop a form of seborrheic dermatitis known as “cradle cap,” which tends to resolve within the first year. The condition is also more common among young adults and middle-aged adults, with males being more prone to the condition than females. However, it can occur in any age group, including older people.
Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Genetic Predispositions
Although the precise origin of seborrheic dermatitis is yet to be completely deciphered, it’s believed to stem from a blend of factors. As it tends to run in families, genetic predispositions suggest that seborrheic dermatitis may be hereditary. The role of hormones is also evident as the condition often develops during hormonal changes like puberty.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors also play a role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis. For instance, it has been observed that the condition often worsens in the winter and dry, cold weather. Stress and fatigue can also trigger or worsen symptoms.
Connection with Other Health Conditions
There is a strong association between seborrheic dermatitis and certain medical conditions. For example, it is more common in individuals with HIV, Parkinson’s, and other neurological disorders. Malassezia, which lives on the skin, has been linked to an overactive immune response to a type of yeast.
Diagnosis and Treatment
How Seborrheic Dermatitis Is Diagnosed
An accurate diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is typically made based on a comprehensive review of the patient’s medical history, a physical exam, and the appearance and location of the rash. In uncommon instances, a skin biopsy might be necessary to eliminate the possibility of other skin disorders. A healthcare provider or dermatologist can make this diagnosis during an appointment.
Standard Treatments for Seborrheic Dermatitis
The management of seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp and other impacted skin areas typically entails using antifungal shampoos, creams, or lotions, aiding in reducing inflammation and production of scales. Active ingredients may include ketoconazole, zinc pyrithione, or selenium sulphide. Topical corticosteroids can be used for short periods to manage flare-ups, while topical antifungals and Calcineurin inhibitors can help manage long-term symptoms. Mild baby shampoo can help loosen and remove scales on the scalp for infants.
Role of Dermatologists in the Treatment Process
Dermatologists play a crucial role in managing seborrheic dermatitis, from diagnosing the condition to providing treatment options and monitoring the patient’s progress. Dermatologists can tailor a treatment strategy based on the specific symptoms and lifestyle of the individual, vigilantly observe for any possible side effects, and make essential modifications to the treatment plan as time progresses.
Strategies for Managing and Preventing Seborrheic Dermatitis
Lifestyle Changes
Some lifestyle changes can help manage seborrheic dermatitis. These include reducing stress, washing the affected areas daily with gentle cleansers, and avoiding potential allergens or irritants in personal care products. Exposure to sunlight and outdoor activities can also help improve symptoms.
Dietary Recommendations
While no specific diet is prescribed for seborrheic dermatitis, a balanced diet rich in essential fatty acids (such as Omega-3 in fish oil, flaxseeds, and walnuts) may help improve skin health and reduce inflammation.
Skincare Regimen
A consistent skincare regimen can help manage and prevent flare-ups. This encompasses consistently cleaning the impacted areas to eliminate surplus oil, utilizing medicated creams or lotions as directed, and steering clear of strong or perfumed skincare items that could provoke irritation or allergic responses.
Impact of Seborrheic Dermatitis on Quality of Life
Psychological Aspects and Self-esteem
Like many skin conditions, seborrheic dermatitis can significantly impact a person’s self-esteem and psychological well-being. The visible nature of the condition, particularly when it affects the face and scalp, can cause embarrassment and social isolation.
Interference with Daily Activities
Flare-ups of seborrheic dermatitis can be uncomfortable and distracting, potentially interfering with daily activities. The need for ongoing treatment can also be time-consuming and disruptive.
Recent Developments in Seborrheic Dermatitis Research
Current Ongoing Clinical Trials
Numerous clinical trials are ongoing, aiming to understand the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis better and develop more effective treatments. These include studies investigating the role of the immune system and skin-barrier dysfunction in the condition and the potential benefits of various medications and phototherapy.
Promising Treatments on the Horizon
Research is underway to develop new and more effective treatment options. These include potential topical treatments that target the Malassezia yeast more effectively and have fewer side effects and immunomodulatory therapies to manage the underlying inflammation.
Q&A
What is Adult seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Adult seborrhoeic dermatitis is a common skin condition that primarily affects the scalp but can also occur on other oily body parts. Red, scaly patches and dandruff characterize it.
Is using counter-dandruff shampoos for seborrhoeic dermatitis a good idea? Yes, it is a common treatment approach. Over-the-counter dandruff shampoos containing zinc, pyrithione, salicylic acid, or coal tar can help reduce symptoms.
What causes seborrhoeic dermatitis?
The exact cause of seborrhoeic dermatitis is unknown, but it’s believed to involve a combination of an overactive immune response to a type of yeast present on the skin, overproduction of oil by the skin’s sebaceous glands, and potential genetic factors.
Are there any associated risk factors for developing seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Yes, several factors may increase your risk of developing seborrhoeic dermatitis, including having a chronic condition such as HIV or Parkinson’s disease, a weakened immune system, certain neurological conditions, or even stress and fatigue.
Can severe cases of seborrhoeic dermatitis lead to hair loss?
While seborrhoeic dermatitis primarily affects the scalp’s surface, severe and untreated cases may cause temporary hair loss due to inflammation around the hair follicles. However, this hair loss is usually reversible once the condition is effectively treated.
Are certain parts of the body more prone to seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Yes, seborrhoeic dermatitis often affects the scalp but can also occur on other body parts where there are many oil glands, like the face, upper chest, back, and creases of the arms and legs.
How can I manage the itchy skin associated with seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Avoid scratching as it can worsen the inflammatory response and potentially lead to infection. Over-the-counter remedies, such as aloe vera lotion or creams containing coal tar or salicylic acid, can help soothe the itchiness. Nevertheless, it is always advisable to seek the advice of a healthcare provider before initiating any new treatment approach.
Is seborrhoeic dermatitis a form of eczema?
Yes, seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes known as seborrhoeic eczema, is a type of chronic eczema that primarily affects oily areas of the body.
What are the potential side effects of long-term use of medicated shampoo for seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Side effects can include skin dryness, irritation, or allergic reaction. Some medicated shampoos may also lead to hair discoloration if used for a long time. Following your healthcare provider’s instructions is important to minimize potential side effects.
How can I reduce the oiliness of my skin to help manage seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Regular cleansing with a mild, non-soap cleanser can help reduce oiliness. Avoid heavy or greasy skincare products that may clog pores and exacerbate symptoms. Discuss with a healthcare provider for personalized skincare advice.
Are there any natural remedies for seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Certain natural solutions, like aloe vera and tea tree oil, have been noted to offer relief to some individuals. A warm water rinse with apple cider vinegar or a scalp massage with olive oil can also be beneficial. Before initiating any new treatment, always confer with a healthcare provider.
What role does ultraviolet light play in treating seborrhoeic dermatitis?
The use of narrowband UVB light, a type of ultraviolet (UV) light, can aid in reducing inflammation and slowing the proliferation of skin cells, thereby relieving seborrhoeic dermatitis. However, UV light therapy should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider due to the risk of skin damage with overexposure.
Can seborrhoeic dermatitis cause problems in the ear canal?
Yes, seborrhoeic dermatitis can affect the ear canal, leading to discomfort, itching, and flaking. It’s recommended to consult a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment.
How long does a typical flare-up of seborrhoeic dermatitis last?
The length of a flare-up can differ, ranging from a few days to several weeks, depending on the severity of the condition and the efficacy of the treatment. Proper management can help to reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Does the American Academy of Dermatology provide information on seborrhoeic dermatitis?
Yes, the American Academy of Dermatology provides a wealth of information on seborrhoeic dermatitis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and tips for managing the condition.
How does a doctor typically diagnose seborrheic dermatitis?
Doctors usually diagnose seborrheic dermatitis based on the appearance and location of the affected skin. Occasionally, a skin biopsy might be performed to eliminate other skin issues exhibiting similar symptoms. It’s important to note that seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic form of eczema that can appear on the scalp, behind the ears, on the hairline, and in other oily areas of the body.
Can individuals with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or Parkinson’s disease have more severe symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis?
Yes, individuals with HIV or Parkinson’s disease may experience more severe cases of seborrheic dermatitis. This is likely due to changes in the immune system and sebum levels associated with these conditions. These individuals should always work closely with their doctors to manage their skin problems effectively, as certain medicines can have serious side effects.
Is seborrheic dermatitis related to fungal infection?
Seborrheic dermatitis is believed to be linked to an overactive immune response to a type of yeast called Malassezia, which naturally resides on the skin’s surface. While not technically a fungal infection, yeast plays a role in developing this skin condition. Seborrheic dermatitis can be effectively managed in mild cases with over-the-counter treatments, while more severe cases may require prescription medicines.
Conclusion
Tips for Living with Seborrheic Dermatitis
Living with seborrheic dermatitis requires a comprehensive management approach, including regular use of prescribed treatments, a healthy lifestyle, and consistent skincare. Patient education and self-care practices play an important role in managing the condition.
The Importance of Seeking Professional Medical Assistance
While home remedies can provide temporary relief, seeking professional medical assistance for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is important. Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic and often lifelong condition, but patients can lead a normal and healthy life with the right treatment and management strategies.
Book Your Free Consultation Today Or Call (647) 492-9093
Comments are closed.